CBD To Reduce Swelling From Injuries And Inflammation
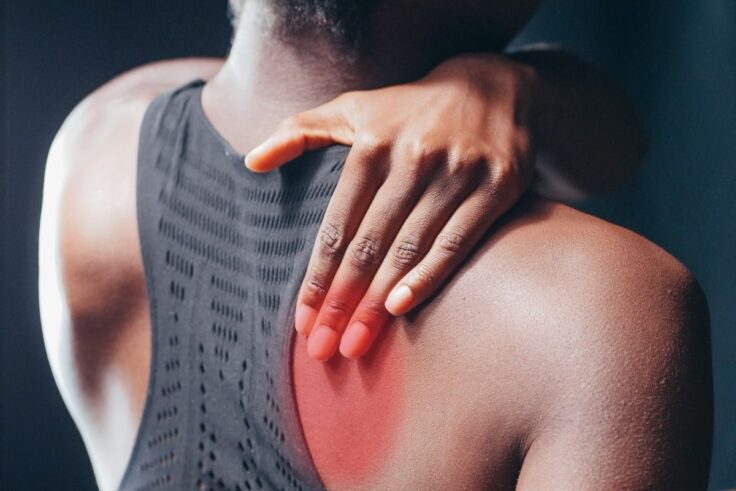
Most scientific research highlights the potential of CBD to reduce swelling from physical injuries and inflammatory disorders. Here’s how this works.
If you live with chronic pain or inflammation from disorders like tendonitis, arthritis, gout, or even recent sports injuries, you might consider CBD’s well-documented anti-inflammatory potential before your next trip to the pharmacy for COX-2 inhibitors, antileukotrienes, NSAIDs, or other synthetic drugs.
After all, these drugs have gained significant notoriety over the past few decades for their high rates of side effects. The most common side effects include intense abdominal pain, rhinitis, and vomiting.
Aside from its lack of debilitating side effects, CBD carries the added benefits of convenience, portability, and versatility.
It can be infused into recovery balms for immediate post-workout use at the boxing gym, for instance. It can be vaped on the go, or even mixed into food or beverages.
Whether it’s from high-CBD strains of cannabis, full-spectrum CBD concentrate, or the strongest CBD oil you can buy, this popular cannabinoid can significantly ameliorate the swelling and pain from inflammatory disorders or physical injuries via its interaction with the endogenous cannabinoid system, or ECS.
What Is The Endocannabinoid System And How Does It Work?
The ECS is in part comprised of a network of cannabinoid receptors found throughout the body, including lymph nodes and fascia.
The numerous receptors that make up the ECS affect the production, throughput, and uptake of hormones and neurotransmitters into the brain.
The two most notable groups of ECS receptors involved in this function are:
- CB1: receptors that are primarily located within the nervous system
- CB2: receptors concentrated within peripheral organs and the immune system
The reason CBD stands out among other cannabinoids in terms of medicinal and therapeutic potential is its modulatory influence on the ECS.
Given its ability to regulate the flow of serotonin or dopamine into the brain, CBD can have positive effects on the symptoms of many common neurophysiological conditions — including chronic pain, inflammation, or even depression.
How Does CBD’s Interaction With The ECS Affect Swelling?
Inflammation is a process wherein signaling molecules known as eicosanoids trigger a normal inflammatory response in specific circumstances, such as in the event of blunt force trauma or infection.
Experts at Reakiro explain that CBD can reduce chronic or abnormal onsets of swelling, as in the case of common inflammatory disorders, by inhibiting the eicosanoid enzyme cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2).
Another important anti-inflammatory function observed in CBD interactions with the ECS is its ability to reduce the body’s response to cytokines, a group of glycoproteins and peptides with a central role in our inflammatory response.
Cytokines are a category of signaling molecules that are rapidly released to the site of injury or infection, regulating immunity, inflammation, and hematopoiesis throughout the healing process.
Understandably, irregular cytokine activity is a hallmark of painful inflammatory disorders like gout, which can be triggered by as little as an excess of dietary carbohydrates.
Because pain is a fairly common symptom of inflammatory disorders, CBD’s documented analgesic potential makes it doubly beneficial.
Until more research around CBD is completed to determine the future of anti-inflammatory drugs, individuals suffering from related chronic conditions should consider the regular use of CBD as a supplement.